文章目录
- spring6
- 1. 一些基本的概念、优势
- 2. 入门案例实现
- maven聚合工程创建步骤
- 分析实现过程
- 3. IoC(Inversion of Control)
- 基于xml的bean环境搭建
- 获取bean
- 获取接口创建实现类
- 依赖注入 setter注入 和 构造器注入
- 原生方式的setter注入
- 原生方式的构造器注入
- 使用bean的方式进行依赖注入步骤
- 对象类型属性赋值步骤
- 引入外部属性文件步骤
- bean的八大生命周期(重要)
- 基于xml的bean自动装配
- 基于注解的bean自动装配(极其重要)
- 使用注解创建对象
- 手动实现IoC
- 实现过程
- 手动实现一个IoC反射
- 手动实现属性注入过程
- 4. 面向切面编程
- 静态代理图解
- 静态代理术语
- 动态代理
- 动态代理的实现过程
- 概念
- 相关术语
- AOP思想综述
- 基于注解方式配置AOP
- 通知类型及其使用
- bean配置文件
- 测试文件
- 报错信息解决
- 重用切入点表达式
- 5. 单元测试
- 6. 事务
- JdbcTemplate对象操作Mysql数据库(Spring事务处理前置知识)
- 准备环境
- 利用JdbcTemplate对象完成对数据库的增加、修改、删除操作
- 利用JdbcTemplate对象完成对数据库的查询操作
- 报错信息解决
- 事务处理
- 概念
- 特性
- 声明式事务管理(基于注解实现)
- 准备环境(基于上面的JDBC示例进行添加,目录结构如下)
- BookController
- BookDao
- BookDaoImpl
- BookService
- BookServiceImpl
- TestBookTx
- 分析
- 开启事务步骤(使用注解的方式)
- 事务注解的一些属性
- Resoource资源操作
- UrlResource实现类访问url资源
- ClassPathResourceDemo访问本地资源(项目内资源)
- loadAndReadUrlResource访问磁盘内文件
- 国际化:i18n
- 数据校验
- 通过Validator接口实现数据校验
- 基于注解校验
- 基于方法校验
- 自定义校验
- AOT
导语:感觉自己记得可能不全,所以我找了一篇优秀的笔记
(双手)奉上链接:https://lixx.cn/archives/spring6-2
https://lixx.cn/categories/spring6
spring6_6">spring6
1. 一些基本的概念、优势
主流,轻量级、开源 框架
广义划分:以SpringFirework为核心的Spring技术栈
狭义划分:专指SpringFireWork
两大核心:Ioc和AOP
特点:
- 非侵入式:功能组件使用注解进行标记,简洁。
- 控制反转:自动创建对象,让我们享受资源注入。
- 面向切面编程:在不修改源代码的基础上增强代码功能。
- 组件化:拆分复杂应用为多个组件共同实现
- 一站式:在集合许多依赖
2. 入门案例实现
maven聚合工程创建步骤

- 引入spring相关依赖
<dependencies>
<!--引入spring-context依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>6.1.10</version>
</dependency>
<!--测试依赖:junit-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-api</artifactId>
<version>5.10.2</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
- 创建类,定义属性和方法
package com.itchen.spring6;
public class User {
public void add(){
System.out.println("add ...");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
User user = new User();
user.add();
}
}
-
按照spring要求创建一个配置文件.xml
-
在配置文件中创建相应的配置信息
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!--下面是一些对标签的约束-->
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--
完成对User对象的创建
id属性:唯一标识 (为了方便一般使用类的首字母小写)
class:要创建的类的对象的全路径(包名称 + 类名称)
-->
<bean id="user" class="com.itchen.spring6.User"></bean>
</beans>
- 最终测试
package com.itchen.spring6;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class TestUser {
@Test
public void testUserObject(){
// 加载spring配置文件,对象创建
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
// 获取创建的对象
User user = (User)context.getBean("user");
System.out.println(user);
// 使用对象的调用方法进行测试
user.add();
}
}
- 输出了user对象的全路径和user的地址
分析实现过程
- 执行了实体类的无参数构造方法
- 如何返回创建的对象
- 加载bean.xml配置文件
- 对xml文件进行解析操作
- 获取标签的属性值
- 使用反射根据类的全路径创建对象
- 对象存放在项目的一个Map集合中;格式<key,value>
3. IoC(Inversion of Control)
Spring通过loC容器来管理所有Java对象的实例化和初始化,控制对象与对象之间的依赖关系。我们将由loC容器管理的Java对象称为Spring Bean,它与使用关键字new创建的Java对象没有任何区别。
将对象的创建和对象与对象的关系都交给了容器进行管理。
基于xml的bean环境搭建
- 将子模块pom文件中的依赖放在父模块中(子模块依然可以调用相应的依赖)
- 创建资源文件(.xml)和java实体类
获取bean
- 实体类user.java
package com.itchen.spring6.iocxml;
public class User {
private String name;
private Integer age;
public void run(){
System.out.println("run ...");
}
}
- bean资源文件获取
- 注意:此时的class类型的bean只能有一个
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="user" class="com.itchen.spring6.iocxml.User"></bean>
</beans>
- 测试获取bean的三种方式
package com.itchen.spring6.iocxml;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class TestUser {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
// 根据对象获取bean
User user = (User)context.getBean("user");
System.out.println("根据id获取bean:" + user);
// 根据类型获取bean
User user2 = (User)context.getBean(User.class);
System.out.println("根据类型获取bean:" + user2);
// 根据id和类型获取bean
User user3 = (User)context.getBean("user", User.class);
System.out.println("根据id和类型获取bean:" + user3);
}
}
获取接口创建实现类
- 创建接口,声明需要实现的方法;在实体类中实现接口。
- 在bean.xml中配置相应的impl实现类
<bean id="USerDaoImpl" class="com.itchen.spring6.iocxml.bean.USerDaoImpl"></bean>
注意:这里的bean必须是唯一的。一个接口只能由一个impl实体类来实现
依赖注入 setter注入 和 构造器注入
原生方式的setter注入
先在类中定义基本的set和get方法,然后在其他类中创建类的对象,调用其setget方法来传值。
原生方式的构造器注入
先定义基本的有参构造器和无参构造器,然后在创建对象的时候在构造器中传入相对应的值。
使用bean的方式进行依赖注入步骤
- 创建一个类,在其中定义基本属性,生成set方法
- 在spring中进行配置
<bean id="book" class="com.itchen.spring6.iocxml.di.Book">
<property name="bname" value="java后端开发"></property>
<property name="author" value="陈志伟"></property>
</bean>
- 测试
@Test
public void testSetter(){
// 1. 加载配置文件
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean-di.xml");
Book book = context.getBean("book", Book.class);
System.out.println(book);
}
or
- 创建类,定义属性,生成有参数的构造方法
- 进行配置
<bean id="BookConstructor" class="com.itchen.spring6.iocxml.di.Book">
<constructor-arg name="bname" value="前端开发"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="author" value="陈志伟"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
- 测试
注意:setter注入调用的是无参构造方法,而构造器注入调用的是有参构造方法
对象类型属性赋值步骤
- 准备工作:创建两个类(班和学生),学生中定义班的对象。定义其中的构造方法、和get、set方法
- 创建bean.xml(名字任意)
<!--第一种方式:引入外部bean的方式-->
<bean id="class" class="com.itchen.spring6.iocxml.ditest.Class">
<property name="cname" value="241班"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="student" class="com.itchen.spring6.iocxml.ditest.Student">
<property name="sname" value="Aim"></property>
<property name="age" value="22"></property>
<property name="cls" ref="class"></property>
</bean>
<!--第二种方式:引入内部bean的方式-->
<bean id="student2" class="com.itchen.spring6.iocxml.ditest.Student">
<property name="sname" value="Mary"></property>
<property name="age" value="20"></property>
<!--内部bean-->
<property name="cls">
<bean id="class2" class="com.itchen.spring6.iocxml.ditest.Class">
<property name="cname" value="242班"></property>
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
<!--第三种方式:级联属性赋值-->
<bean id="cls3" class="com.itchen.spring6.iocxml.ditest.Class">
<property name="cname" value="144班"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="student3" class="com.itchen.spring6.iocxml.ditest.Student">
<property name="sname" value="Tom"></property>
<property name="age" value="28"></property>
<property name="cls" ref="class"></property>
<!--级联再赋值-->
<property name="cls.cname" value="141班"></property>
</bean>
<!--第四种方式:数组注入-->
<!--注入数组类型的属性-->
<bean id="clss" class="com.itchen.spring6.iocxml.ditest.Class">
<property name="cname" value="143班"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="student" class="com.itchen.spring6.iocxml.ditest.Student">
<!--普通-->
<property name="sname" value="Aim"></property>
<property name="age" value="22"></property>
<!--对象-->
<property name="cls" ref="clss"></property>
<!--数组-->
<property name="loves">
<array>
<value>吃饭</value>
<value>睡觉</value>
<value>玩jj</value>
</array>
</property>
</bean>
<!--第五种方式:集合类型属性的注入-->
<bean id="studen1" class="com.itchen.spring6.iocxml.ditest.Student">
<property name="sname" value="Aim"></property>
<property name="age" value="19"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="studen2" class="com.itchen.spring6.iocxml.ditest.Student">
<property name="sname" value="Mary"></property>
<property name="age" value="19"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="studen3" class="com.itchen.spring6.iocxml.ditest.Student">
<property name="sname" value="Tom"></property>
<property name="age" value="19"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="cls" class="com.itchen.spring6.iocxml.ditest.Class">
<property name="cname" value="142班"></property>
<property name="stuList">
<list>
<ref bean="studen1"></ref>
<ref bean="studen2"></ref>
<ref bean="studen3"></ref>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
注意:因为这里的包含关系变了,需要修改一下测试方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean-diarr.xml");
// 学生的对象
Student stu = context.getBean("student",Student.class);
stu.work();
}
<!--第六种方式:map类型属性注入-->
<!--
1. 创建两个对象:用bean标签进行配置
2. 注入它的普通类型的属性
3. 在学生的bean中注入map集合的属性
-->
<bean id="teacher" class="com.itchen.spring6.iocxml.dimap.Teacher">
<property name="tid" value="1000"></property>
<property name="tname" value="小李"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="student" class="com.itchen.spring6.iocxml.dimap.Student">
<property name="sid" value="2000"></property>
<property name="sname" value="小明"></property>
<property name="teacherMap">
<map>
<entry>
<key>
<value>10010</value>
</key>
<!--这里的(键值对的值)值如果是一个普通的值,可以使用value-->
<ref bean="teacher"></ref>
</entry>
</map>
</property>
</bean>
<!--第七种方式:集合类型的属性注入-->
<!--
1. 创建三个对象
2. 注入普通类型的属性
3. 使用“util:类型” 定义
4. 在学生bean中引入3.的bean
-->
<bean id="student" class="com.itchen.spring6.iocxml.dimap.Student">
<property name="sid" value="10000"></property>
<property name="sname" value="张三"></property>
<!--注入list和map类型属性-->
<property name="lessonList" ref="lessonList"></property>
<property name="teacherMap" ref="teacherMap"></property>
</bean>
<util:list id="lessonList">
<ref bean="lesson1"></ref>
<ref bean="lesson2"></ref>
</util:list>
<util:map id="teacherMap">
<entry>
<key>
<value>10010</value>
</key>
<ref bean="teacher1"></ref>
</entry>
<entry>
<key>
<value>10086</value>
</key>
<ref bean="teacher2"></ref>
</entry>
</util:map>
<bean id="lesson1" class="com.itchen.spring6.iocxml.dimap.Lesson">
<property name="lessonName" value="java开发"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="lesson2" class="com.itchen.spring6.iocxml.dimap.Lesson">
<property name="lessonName" value="前端开发"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="teacher1" class="com.itchen.spring6.iocxml.dimap.Teacher">
<property name="tname" value="西门庆"></property>
<property name="tid" value="1000"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="teacher2" class="com.itchen.spring6.iocxml.dimap.Teacher">
<property name="tname" value="欧阳弧"></property>
<property name="tid" value="2000"></property>
</bean>
注意:第七种方式在使用的时候需要引入标签相应的命名空间
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
引入外部属性文件步骤
- 引入外部属性文件的相关依赖【pom文件】
- 创建一个外部的属性文件。定义数据信息:用户名、密码、地址。【.properties文件】
- 创建spring的配置文件,引入context的命名空间。引入属性文件,使用表达式完成注入。
<!--引入外部文件 完成数据库的信息注入-->
<bean id="druidDataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"></property>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.user}"></property>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"></property>
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driver}"></property>
</bean>
bean的八大生命周期(重要)
可以在配置文件中【bean.xml文件】使用参数的形式制定bean对象的初始化函数和销毁函数。
- bean对象的创建(调用无参构造方法)
- 给bean对象设置相关属性
- bean后置处理器(初始化之前)
- bean对象初始化(调用制定的初始化方法)
- bean后置处理器(初始化之后)
- bean对象创建完成了,可以使用了
- bean对象销毁(配置制定的销毁方法)
- IoC容器关闭
基于xml的bean自动装配
<!--根据类型自动装配-->
<bean id="userController" class="com.itchen.spring6.iocxml.auto.Controller.UserController" autowire="byType"></bean>
<bean id="userService" class="com.itchen.spring6.iocxml.auto.Service.UserServiceImpl" autowire="byType"></bean>
<bean id="userDao" class="com.itchen.spring6.iocxml.auto.dao.UserDaoImpl" autowire="byType"></bean>
<!--根据名称自动装配-->
<bean id="userController" class="com.itchen.spring6.iocxml.auto.Controller.UserController" autowire="byName"></bean>
<bean id="userService" class="com.itchen.spring6.iocxml.auto.Service.UserServiceImpl" autowire="byName"></bean>
<bean id="userDao" class="com.itchen.spring6.iocxml.auto.dao.UserDaoImpl" autowire="byName"></bean>
<!--这时需要保证类的名字和id的名字一模一样-->
基于注解的bean自动装配(极其重要)
使用注解创建对象
- 引入依赖
- 开启组件扫描
<context:component-scan base-package="com.itchen.spring6"></context:component-scan>
- 被扫描的类用
@component修饰;自动注入的属性用@Autowired修饰;使用注解定义bean
| 注解 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| @Component | 该注解用于描述 Spring 中的 Bean,它是一个泛化的概念,仅仅表示容器中的一个组件(Bean),并且可以作用在应用的任何层次,例如 Service 层、Dao 层等。 使用时只需将该注解标注在相应类上即可。 |
| @Repository | 该注解用于将数据访问层(Dao 层)的类标识为 Spring 中的 Bean,其功能与 @Component 相同。 |
| @Service | 该注解通常作用在业务层(Service 层),用于将业务层的类标识为 Spring 中的 Bean,其功能与 @Component 相同。 |
| @Controller | 该注解通常作用在控制层(如SpringMVC 的 Controller),用于将控制层的类标识为 Spring 中的 Bean,其功能与 @Component 相同。 |
手动实现IoC
主要使用java的反射机制和注解进行实现
实现过程
- 创建子模块
- 创建测试类
- 创建两个注解
- 约定注解@Bean @Di
- 创建bean容器的接口ApplicationContext,定义方法,返回对象
- 实现bean的容器接口
- 返回对象
- 根据包的规则加载bean(设置包的扫描规则)
手动实现一个IoC反射
loadBean步骤:
// 1. 判断当前是否是文件夹
// 2. 获取文件夹里面的所有内容
// 3. 文件夹里面为空,直接返回
// 4. 如果文件夹里面不为空
// 遍历得到的每个file对象 重复3. 4.// 5. 如果是文件,得到包路径 + 类名称
// 6. 判断文件是否是.class类型,如果是,则去掉后缀
// 7. 如果有@Bean注解使用反射实例化
// 将实例化结果放入map集合中
package com.itchen.bean;
import com.itchen.annotation.Bean;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URL;
import java.net.URLDecoder;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class AnnotationApplicationContext implements ApplicationContext{
// 创建map集合用于创建bean的实例对象
private static Map<Class,Object> beanFactory = new HashMap<>();
private static String rootPath;
// 返回对象
@Override
public Object getBean(Class clazz) {
return beanFactory.get(clazz);
}
// 设置包的扫描规则
// 创建有参构造,传递包路径
public static void pathDemo1(String basePackage){
// 把点替换为反斜杠
String packagePath = basePackage.replaceAll("\\.", "\\\\");
// 获取包的绝对路径
try {
Enumeration<URL> dirs = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().getResources(packagePath);
while(dirs.hasMoreElements()){
URL url = dirs.nextElement();
String filePath = URLDecoder.decode(url.getFile(), "utf-8");
rootPath = filePath.substring(0, filePath.length() - packagePath.length());
System.out.println(filePath);
loadBean(new File(filePath));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
// 包扫描过程,实例化bean
private static void loadBean(File fileParent) throws ClassNotFoundException {
// 1. 判断当前是否是文件夹
if (fileParent.isDirectory()) {
// 2. 获取文件夹里面的所有内容
File[] childrenFiles = fileParent.listFiles();
// 3. 文件夹里面为空,直接返回
if (childrenFiles == null || childrenFiles.length == 0) {
return;
}
// 4. 如果文件夹里面不为空
// 遍历得到的每个file对象 重复3. 4.
for (File child : childrenFiles) {
if (child.isDirectory()) {
loadBean(child);
} else {
// 5. 如果是文件,得到包路径 + 类名称
String pathWithClass = child.getAbsolutePath().substring(rootPath.length() - 1);
// 6. 判断文件是否是.class类型,如果是,则去掉后缀
String fullName = pathWithClass.replaceAll("\\\\", ".").replace(".class", "");
try {
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName(fullName);
// 7. 如果有@Bean注解使用反射实例化
if (!aClass.isInterface()) {
Bean annotation = aClass.getAnnotation(Bean.class);
if (annotation != null) {
Object instance = aClass.newInstance();
if (aClass.getInterfaces().length > 0) {
System.out.println("正在加载【" + aClass.getInterfaces()[0] + "】,实例对象是:" + instance.getClass().getName());
beanFactory.put(aClass.getInterfaces()[0], instance);
} else {
System.out.println("正在加载【" + aClass.getName() + "】,实例对象是:" + instance.getClass().getName());
beanFactory.put(aClass, instance);
}
}
}
// 将实例化结果放入map集合中
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
}
手动实现属性注入过程
// 1. 实例化对象在beanFactory的map集合里面
// 遍历map集合
// 2. 获取所有的value值,获取每个对象的属性
// 3. 遍历对象属性的数组,得到每个属性
// 4. 判断是否有@Di注解
// 5. 如果有,将对象注入
package com.itchen.bean;
import com.itchen.annotation.Bean;
import com.itchen.annotation.Di;
import com.itchen.bean.ApplicationContext;
import java.io.File;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.net.URL;
import java.net.URLDecoder;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class AnnotationApplicationContext implements ApplicationContext {
//存储bean的容器
private HashMap<Class, Object> beanFactory = new HashMap<>();
private static String rootPath;
@Override
public Object getBean(Class clazz) {
return beanFactory.get(clazz);
}
/**
* 根据包扫描加载bean
* @param basePackage
*/
public AnnotationApplicationContext(String basePackage) {
try {
String packageDirName = basePackage.replaceAll("\\.", "\\\\");
Enumeration<URL> dirs =Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().getResources(packageDirName);
while (dirs.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = dirs.nextElement();
String filePath = URLDecoder.decode(url.getFile(),"utf-8");
rootPath = filePath.substring(0, filePath.length()-packageDirName.length());
loadBean(new File(filePath));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
// 属性的注入
loadDi();
}
private void loadBean(File fileParent) {
if (fileParent.isDirectory()) {
File[] childrenFiles = fileParent.listFiles();
if(childrenFiles == null || childrenFiles.length == 0){
return;
}
for (File child : childrenFiles) {
if (child.isDirectory()) {
//如果是个文件夹就继续调用该方法,使用了递归
loadBean(child);
} else {
//通过文件路径转变成全类名,第一步把绝对路径部分去掉
String pathWithClass = child.getAbsolutePath().substring(rootPath.length() - 1);
//选中class文件
if (pathWithClass.contains(".class")) {
// com.xinzhi.dao.UserDao
//去掉.class后缀,并且把 \ 替换成 .
String fullName = pathWithClass.replaceAll("\\\\", ".").replace(".class", "");
try {
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName(fullName);
//把非接口的类实例化放在map中
if(!aClass.isInterface()){
Bean annotation = aClass.getAnnotation(Bean.class);
if(annotation != null){
Object instance = aClass.newInstance();
//判断一下有没有接口
if(aClass.getInterfaces().length > 0) {
//如果有接口把接口的class当成key,实例对象当成value
System.out.println("正在加载【"+ aClass.getInterfaces()[0] +"】,实例对象是:" + instance.getClass().getName());
beanFactory.put(aClass.getInterfaces()[0], instance);
}else{
//如果有接口把自己的class当成key,实例对象当成value
System.out.println("正在加载【"+ aClass.getName() +"】,实例对象是:" + instance.getClass().getName());
beanFactory.put(aClass, instance);
}
}
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException | IllegalAccessException | InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
}
// 属性注入
private void loadDi() {
for(Map.Entry<Class,Object> entry : beanFactory.entrySet()){
//就是咱们放在容器的对象
Object obj = entry.getValue();
Class<?> aClass = obj.getClass();
Field[] declaredFields = aClass.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : declaredFields){
Di annotation = field.getAnnotation(Di.class);
if( annotation != null ){
field.setAccessible(true);
try {
System.out.println("正在给【"+obj.getClass().getName()+"】属性【" + field.getName() + "】注入值【"+ beanFactory.get(field.getType()).getClass().getName() +"】");
field.set(obj,beanFactory.get(field.getType()));
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
}
4. 面向切面编程
核心业务+任务日志 – > 代码冗余
解决:用代理模式将其分离(分离任务日志) ----------------- 解耦
静态代理图解
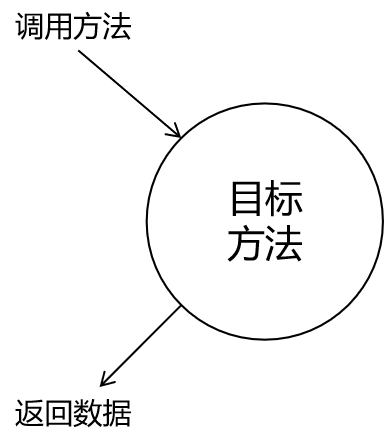
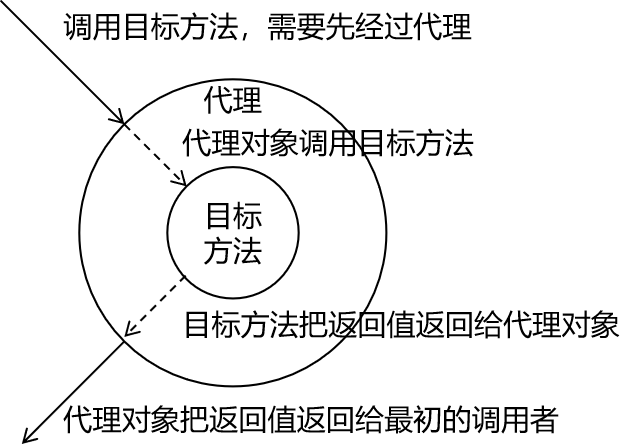
静态代理术语
代理:将非核心代码分离出来后,封装这些非逻辑代理、对象、方法
目标:被代理套用的非核心代码类、对象、方法
动态代理
原因:因为静态代理不具备代码的灵活性,所以引入了动态代理
动态代理的实现过程
package com.itchen.spring6.aop.example;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class ProxyFactory {
// 目标对象
private Object target;
public ProxyFactory(Object obj){
target = obj;
}
// 返回代理对象的方法
public Object getProxy(){
/**
* 参数1. 类加载器
* 参数2. 目标对象实现的所有接口
* 参数3. 设置代理修改目标函数的方法
* */
ClassLoader classLoader = target.getClass().getClassLoader();
Class<?>[] interfaces = target.getClass().getInterfaces();
InvocationHandler invocationHandler = new InvocationHandler(){
@Override
/**
* 参数1. 代理对象
* 参数2. 需要重写目标对象中的方法啊
* 参数3. 目标方法中的参数
* */
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("[动态代理][日志] "+method.getName()+",参数:"+ Arrays.toString(args));
Object result = method.invoke(target, args);
System.out.println("[动态代理][日志] "+method.getName()+",结果:"+ result);
return result;
}
};
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader,interfaces,invocationHandler);
}
}
自行补充计算器的基类和计算器接口类
// 测试类
package com.itchen.spring6.aop.example;
public class TestCaculator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. 创建代理对象
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory(new CalculatorImpl());
Calculator proxy = (Calculator) proxyFactory.getProxy();
proxy.add(1,2);
proxy.mul(2,4);
}
}
概念
AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming)是一种设计思想,是软件设计领域中的面向切面编程,它是面向对象编程的一种补充和完善,它以通过预编译方式和运行期动态代理方式实现,在不修改源代码的情况下,给程序动态统一添加额外功能的一种技术。利用AOP可以对业务逻辑的各个部分进行隔离,从而使得业务逻辑各部分之间的耦合度降低,提高程序的可重用性,同时提高了开发的效率。
相关术语
- 横切关注点
- 项目中相同的需要被提取的部分
- 通知(增强)
- 需要增加的功能
- 通知方法:横切关注点的实现
- 通知类型:五种
- 切面 > 通知
- 封装通知方法的类(eg. 一个切面类包含:前置通知、返回通知、后置通知等)
- 目标
- 被代理的对象
- 代理
- 向目标对象应用通知后创建代理对象
- 连接点
- 能使用通知的地方
- 切入点
- 实际去增强方法的位置
AOP思想综述
将特定的代码封装到切面类中,将切面类用于一个新的目标方法,最终实现 方法的增强(方法的增强好抽象呀)
基于注解方式配置AOP
通知类型及其使用
package com.itchen.spring6.aop.annoaop;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Arrays;
@Aspect // 切面类
@Component // 在spring的ioc容器中进行管理
public class LogAspect {
// 设置切入点和通知类型
@Before(value = "pointCut()")
public void beforeMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint){
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
String args = Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs());
System.out.println("Logger-->前置通知,方法名:"+methodName+",参数:"+args);
}
@After("execution(* com.itchen.spring6.aop.annoaop.CalculatorImpl.*(..))")
public void afterMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint){
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("Logger-->后置通知,方法名:"+methodName);
}
@AfterReturning(value = "execution(* com.itchen.spring6.aop.annoaop.CalculatorImpl.*(..))", returning = "result")
public void afterReturningMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object result){
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("Logger-->返回通知,方法名:"+methodName+",结果:"+result);
}
@AfterThrowing(value = "execution(* com.itchen.spring6.aop.annoaop.CalculatorImpl.*(..))", throwing = "ex")
public void afterThrowingMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint, Throwable ex){
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("Logger-->异常通知,方法名:"+methodName+",异常:"+ex);
}
@Around("execution(* com.itchen.spring6.aop.annoaop.CalculatorImpl.*(..))")
public Object aroundMethod(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint){
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
String args = Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs());
Object result = null;
try {
System.out.println("环绕通知-->目标对象方法执行之前");
//目标对象(连接点)方法的执行
result = joinPoint.proceed();
System.out.println("环绕通知-->目标对象方法返回值之后");
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
throwable.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("环绕通知-->目标对象方法出现异常时");
} finally {
System.out.println("环绕通知-->目标对象方法执行完毕");
}
return result;
}
// 重用切入点表达式
@Pointcut(value = "execution(* com.itchen.spring6.aop.annoaop.CalculatorImpl.*(..))")
public void pointCut(){}
}
bean配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!--开启组件的扫描-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.itchen.spring6.aop.annoaop"></context:component-scan>
<!--开启自动代理-->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy />
</beans>
测试文件
package com.itchen.spring6.aop.annoaop;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class TestAop {
@Test
public void testAdd(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
Calculator calculator = context.getBean(Calculator.class);
calculator.add(1,1);
}
}
报错信息解决
NoSuchBeanDefinitionException:没有在实现类中加入@Component注解创建bean
重用切入点表达式
通知注解后面的参数重复书写,所以可以用注解将参数定义为一个类似宏的东西
5. 单元测试
Junit依赖自动注入方便测试
整合Junit5 和 Junit4
// 不整合的时候测试
public class TestUser {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean-auto.xml");
UserController userController = context.getBean("userController", UserController.class);
userController.addUser();
}
}
// 整合Junit5
@SpringJUnitConfig(locations = "classpath:bean.xml")
public class SpringTestJunit5 {
@Autowired
private User user;
// 测试方法
@Test
public void testUser(){
System.out.println(user);
user.run();
}
}
// 整合Junit4
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:bean.xml")
public class SpringTestJunit4 {
@Autowired
private User user;
@Test
public void testUser4(){
System.out.println(user);
user.run();
}
}
6. 事务
JdbcTemplate对象操作Mysql数据库(Spring事务处理前置知识)
准备环境
- 导入依赖
<!--spring jdbc Spring 持久化层支持jar包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>6.0.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- MySQL驱动 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.30</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 数据源 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.2.15</version>
</dependency>
<!--spring对junit的支持相关依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>6.0.2</version>
</dependency>
<!--junit5测试-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-api</artifactId>
<version>5.9.0</version>
</dependency>
- 配置jdbc.properties配置文件连接数据库
jdbc.user=root
jdbc.password=root
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
- 配置bean.xml配置JdbcTemplate
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!-- 导入外部属性文件 -->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties" />
<!-- 配置数据源 -->
<bean id="druidDataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driver}"/>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.user}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</bean>
<!-- 配置 JdbcTemplate -->
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<!-- 装配数据源 -->
<property name="dataSource" ref="druidDataSource"/>
</bean>
</beans>
利用JdbcTemplate对象完成对数据库的增加、修改、删除操作
测试代码
package com.itchen.spring6.jdbc;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit.jupiter.SpringJUnitConfig;
@SpringJUnitConfig(locations = "classpath:beans.xml")
public class JdbcTemplateTest {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
// 添加、修改、删除操作
@Test
public void testUpdate(){
// 添加数据
String sql = "insert into t_emp values(null,?,?,?)";
Object[] params = {"洛萨",32,"男"};
// 添加数据
// int rows = jdbcTemplate.update(sql,params);
// System.out.println("影响了" + rows + "行");
String sql2 = "update t_emp set name=? where id=?";
// 修改id为?行数据的名字字段
// int row = jdbcTemplate.update(sql2,"666",3);
// System.out.println("影响了" + row + "行");
// 删除id为?的一行
String sql3 = "delete from t_emp where id=?";
// int row3 = jdbcTemplate.update(sql3,3);
// System.out.println("影响了" + row3 + "行");
}
}
利用JdbcTemplate对象完成对数据库的查询操作
package com.itchen.spring6.jdbc;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.RowMapper;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit.jupiter.SpringJUnitConfig;
import java.util.List;
@SpringJUnitConfig(locations = "classpath:beans.xml")
public class jdbcTemplateTest2 {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
/**
* queryForObject
* */
// 查询并获取数据库的第一行数据
@Test
public void testSelectObject1(){
String sql = "select * from t_emp where id=?";
Emp person = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, (rs, rowNum) -> {
Emp emp = new Emp();
emp.setId(rs.getInt("id"));
emp.setName(rs.getString("name"));
emp.setAge(rs.getInt("age"));
emp.setSex(rs.getString("sex"));
return emp;
}, 1);
System.out.println(person);
}
/**
* queryForObject
* */
@Test
public void testSelectObject2(){
String sql = "select * from t_emp where id=?";
// 利用BeanPropertyRowMapper方法自动创建对象接收数据库数据
Emp emp = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(Emp.class),2);
System.out.println(emp);
}
/**
* query
* */
@Test
public void testSelectList(){
String sql = "select * from t_emp";
List<Emp> list = jdbcTemplate.query(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(Emp.class));
System.out.println(list);
}
/**
* queryForObject
* */
//查询单行单列的值
@Test
public void selectCount(){
String sql = "select count(id) from t_emp";
Integer count = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, Integer.class);
System.out.println(count);
}
}
报错信息解决
BadSqlGrammarException:没有按照规定的sql语法进行传递参数信息
事务处理
概念
eg.银行转账,要成功都成功;要失败,都失败
特性
原子性:要成功,都成功
一致性:操作前和操作后总量一致
隔离性:多个事务进行操作,对各个事务之间没有影响
持久性:提交就永久保存
声明式事务管理(基于注解实现)
准备环境(基于上面的JDBC示例进行添加,目录结构如下)
BookController
package com.itchen.spring.tx.controller;
import com.itchen.spring.tx.service.BookService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
@Controller
public class BookController {
@Autowired
private BookService bookService;
// 买书的方法: 图书的id 、 用户的id
public void buyBook(Integer bookId,Integer userId){
// 调用Service方法
bookService.buyBook(bookId,userId);
}
}
BookDao
package com.itchen.spring.tx.dao;
public interface BookDao {
Integer getBookPriceByBookId(Integer bookId);
void updateStock(Integer bookId);
void updateUserBalance(Integer userId,Integer price);
}
BookDaoImpl
package com.itchen.spring.tx.dao;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public class BookDaoImpl implements BookDao{
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
Integer price;
@Override
public Integer getBookPriceByBookId(Integer bookId) {
String sql = "select price from t_book where book_id=?";
price = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, Integer.class, bookId);
return price;
}
@Override
public void updateStock(Integer bookId) {
String sql = "update t_book set stock=stock-1 where book_id=?";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql,bookId);
}
@Override
public void updateUserBalance(Integer userId,Integer price) {
String sql = "update t_user set balance=balance-? where user_id=?";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql,price,userId);
}
}
BookService
package com.itchen.spring.tx.service;
public interface BookService {
void buyBook(Integer bookId, Integer userId);
}
BookServiceImpl
package com.itchen.spring.tx.service;
import com.itchen.spring.tx.dao.BookDao;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class BookServiceImpl implements BookService{
@Autowired
private BookDao bookDao;
@Override
public void buyBook(Integer bookId, Integer userId) {
// 根据图书id查询图书的价格
Integer price = bookDao.getBookPriceByBookId(bookId);
// 更新图书表中的库存量
bookDao.updateStock(bookId);
// 更新用户余额
bookDao.updateUserBalance(userId,price);
}
}
TestBookTx
package com.itchen.spring.tx;
import com.itchen.spring.tx.controller.BookController;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit.jupiter.SpringJUnitConfig;
@SpringJUnitConfig(locations = "classpath:beans.xml")
public class TestBookTx {
@Autowired
private BookController bookController;
@Test
public void testBuyBook(){
bookController.buyBook(1,1);
}
}
分析
将买书一个方法作为一个大的方法在Controller中调用。然后再Service将这个方法分解成多个数据库操作。最后将数据库的各个操作在dao层进行实现。(揉碎了喂到嘴里)
问题:这里如果用户的余额不足,仍然会执行图书出库操作,但是应为没有事物的回滚,报错的步骤不会执行。
开启事务步骤(使用注解的方式)
- 在bean中添加:开启事务的注解驱动
- 在业务逻辑层(Service层)添加事务注解@Transactional**【这个注解可以加在方法上,也可以加在类上】**
运行结果:在用户余额不足的情况下依然报错,但是不会执行图书出库操作
事务注解的一些属性
| 参数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| readOnly | 是否只读(表示是否只能进行查询操作) |
| timeout | 设置超时时间(-1,表示永不超时;单位是秒) |
| noRollbackFor | 事务策略(设置哪些异常不回滚) |
| (见文章头连接) | 隔离级别:解决脏读、不可重读、虚读等 |
| (见文章头连接) | 传播行为:事务之间的相互调用,使用哪一个事务进行逻辑处理 |
脏读:两个都未提交,但是都能看见对方的修改
不可重复:一个提交了,另一个修改了没有提交的能看到修改完成之后的数据
虚读:一个提交了,另一个做完了添加没有提交之后能读到自己添加的数据
Resoource资源操作
Resource接口提供了对低级资源访问的抽象方法,接口有多个实现类供给给我们来访问低级资源
UrlResource实现类访问url资源
// 演示urlResource访问网络资源
public class UrlResourceDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// http前缀
loadUrlResource("https://www.baidu.com/");
// file前缀 放在项目的根路径
loadUrlResource("file:itchen.txt");
}
// 访问前缀http
public static void loadUrlResource(String path){
// 创建Resource接口的实现类的对象
try {
// 获取资源
UrlResource url = new UrlResource(path);
System.out.println(url.getFilename());
System.out.println(url.getURI());
System.out.println(url.getDescription());
System.out.println(url.getInputStream().read());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
// 获取资源信息
}
}
ClassPathResourceDemo访问本地资源(项目内资源)
// 访问类路径下的资源
public class ClassPathResourceDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
loadClasspathResource("itchen.txt");
}
public static void loadClasspathResource(String path){
// 创建的对象
ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource(path);
System.out.println(resource.getFilename());
System.out.println(resource.getDescription());
// 获取文件内容
try {
InputStream in = resource.getInputStream();
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
while(in.read(b) != -1){
System.out.println(new String(b));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
loadAndReadUrlResource访问磁盘内文件
public class FileSystemResourceDemo {
public static void loadAndReadUrlResource(String path) throws Exception{
//相对路径
FileSystemResource resource = new FileSystemResource("itchen.txt");
//绝对路径
//FileSystemResource resource = new FileSystemResource("D:\\itchen.txt");
// 获取文件名
System.out.println("resource.getFileName = " + resource.getFilename());
// 获取文件描述
System.out.println("resource.getDescription = "+ resource.getDescription());
//获取文件内容
InputStream in = resource.getInputStream();
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
while(in.read(b)!=-1) {
System.out.println(new String(b));
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
loadAndReadUrlResource("itchen.txt");
}
}
其他的实现类见文档头链接
国际化:i18n
调用不同的配置文件示例
@Test
public void test1(){
ResourceBundle bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("itchen", new Locale("zh", "CN"));
String value1 = bundle.getString("test");
System.out.println(value1);
}
@Test
public void test2() {
ResourceBundle bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("itchen", new Locale("en", "GB"));
String value1 = bundle.getString("test");
System.out.println(value1);
}
数据校验
通过Validator接口实现数据校验
public class TestMethod1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建person对象
Person person = new Person();
person.setName("lucy");
person.setAge(-1);
// 创建Person对应的DataBinder
DataBinder binder = new DataBinder(person);
// 设置校验
binder.setValidator(new PersonValidator());
// 由于Person对象中的属性为空,所以校验不通过
binder.validate();
//输出结果
BindingResult results = binder.getBindingResult();
System.out.println(results.getAllErrors());
}
}
测试:
public class PersonValidator implements Validator {
// 校验类型确认
@Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> clazz) {
return Person.class.equals(clazz);
}
// 校验逻辑
@Override
public void validate(Object object, Errors errors) {
ValidationUtils.rejectIfEmpty(errors, "name", "name.empty");
Person p = (Person) object;
if (p.getAge() < 0) {
errors.rejectValue("age", "error value < 0");
} else if (p.getAge() > 110) {
errors.rejectValue("age", "error value too old");
}
}
}
基于注解校验
基于方法校验
自定义校验
其他的实现类见文档头链接
AOT
AOT先关概念
-
JIT:动态编译,边运行边编译
-
AOT:运行前编译,提前编译